Applications
Applications
Our organisation categorises electrical components based on specific purposes and voltage criteria, simplifying their selection for diverse applications.
 Transformer Oil Filtration
Transformer Oil Filtration

Transformer oil filtration is a crucial maintenance process used to extend the lifespan and enhance the efficiency of transformers. This process involves removing impurities such as water, gas, and particulate matter from the insulating oil.
 Common Contaminants in Transformer Oil
Common Contaminants in Transformer Oil

Transformer oil can deteriorate over time due to contamination from various external and internal sources. These contaminants adversely affect the oil’s insulating and cooling properties, leading to reduced transformer performance and possible failures. Identifying and controlling these impurities is essential to ensure safe and efficient transformer operation.
Moisture can enter the oil from humidity or leaks and can cause a decrease in dielectric strength.
Over time, oil can absorb gases like hydrogen, which can indicate internal transformer issues like arcing or overheating.
Dust and other fine particles can contaminate the oil during operation or maintenance, which can wear down transformer components.
 Why- Transformer Oil Filtration?
Why- Transformer Oil Filtration?

Transformer oil filtration is essential for several critical reasons, all of which contribute to the safe and efficient operation of transformers. Here’s why it’s necessary:
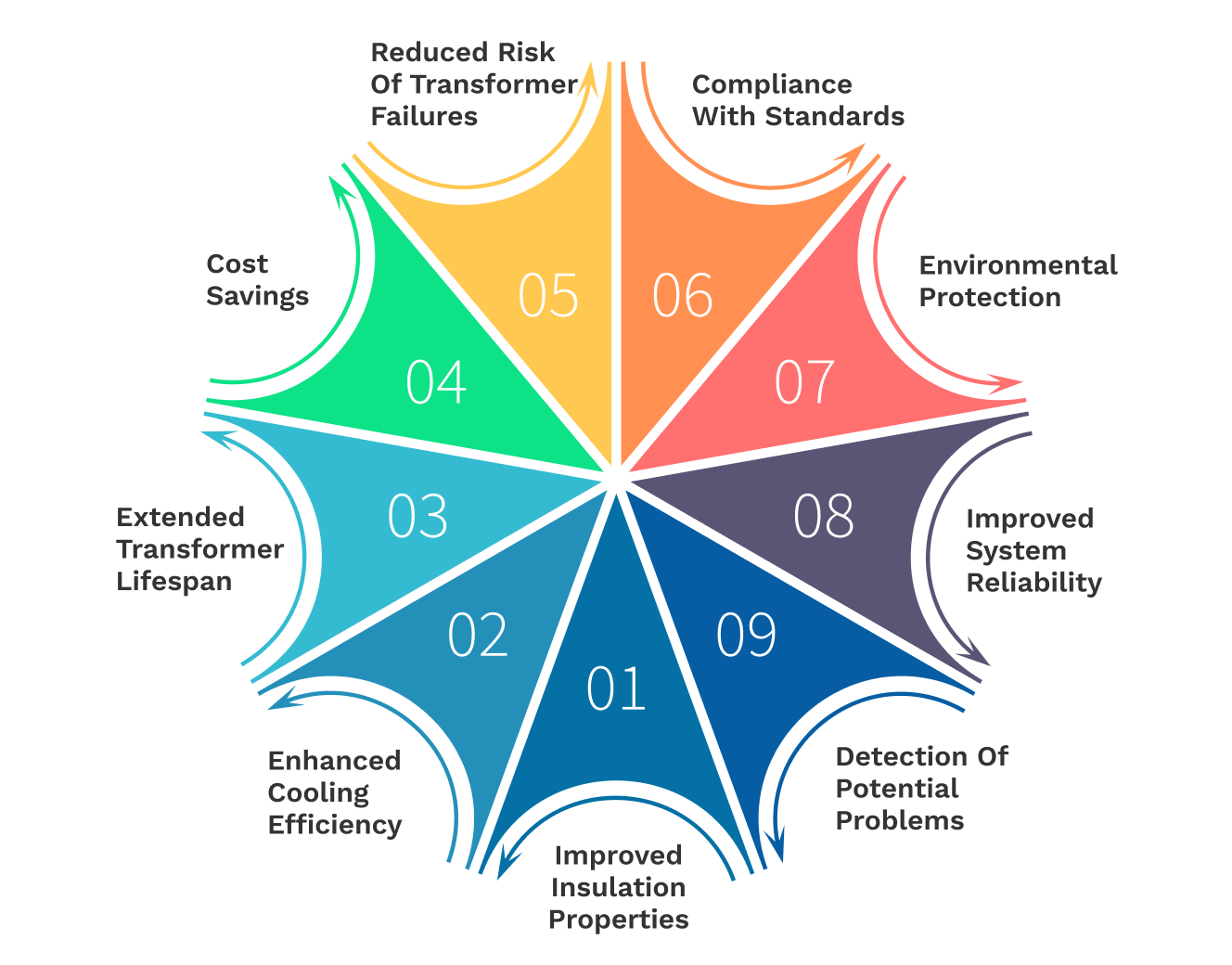
Transformer oil insulates internal components, preventing electrical failure. Oil can become polluted with water, gasses, and other particulates, reducing its insulation. Filtration removes impurities and restores oil's insulation.
Cooling the transformer's core and coils need transformer oil beyond insulation. Contaminated oil absorbs and dissipates heat less, causing overheating and transformer failure. Clean oil maximizes cooling and heat transfer.
Transformer oil often contains dangerous water. It diminishes oil dielectric strength and can cause partial discharges or electrical arcs that damage the transformer's internal structure. Filtration prevents such hazards by removing moisture.
Acids and sludge form from transformer oil oxidation. Byproducts can damage transformer parts and reduce oil efficiency. Many filtration technologies eliminate oxidation products and improve oil quality.
Oil filtration maintains transformer components and prevents insulation failure and overheating, extending their lifespan. Maintaining power supply and preventing costly downtimes need this reliability.
Various international and local standards dictate specific requirements for transformer oil quality to ensure safety and performance. Regular filtration helps in maintaining these standards and avoiding penalties or operational restrictions.
Investing in regular transformer oil filtration can be more cost-effective compared to the replacement of the entire transformer. Early detection and removal of contaminants can prevent major failures and the associated high costs.
Preventing transformer leaks and failures through regular maintenance and oil filtration reduces the risk of environmental contamination, which can occur if degraded oil or internal faults lead to leaks.
 Procedure involved in Filtrating Oil of a Transformer.
Procedure involved in Filtrating Oil of a Transformer.

The procedure for transformer oil filtration typically involves several key steps designed to remove impurities such as water, gases, and particulate matter from the oil, thus restoring or maintaining its insulating and cooling properties. Here’s a detailed look at the typical steps involved in the process:
Before starting the filtration process, a sample of the transformer oil is tested to determine the level of contamination. This helps in deciding the extent of filtration needed and assessing the current condition of the oil. Common tests include measuring dielectric strength, water content, and the presence of particulate matter.
Filtration equipment is set up either adjacent to the transformer for offline filtration or connected directly to the transformer for online filtration. The setup includes pumps, filters, heaters, and sometimes, degassing and dehydration units.
The oil is typically heated to reduce its viscosity, which helps in the removal of impurities. Heating makes it easier to extract water and dissolved gases. However, care is taken to keep the temperature well below the oil’s flash point to ensure safety.
In this step, the oil is subjected to a vacuum that helps remove dissolved gases and water vapor. This is often done using a vacuum dehydrator. The reduction in pressure under vacuum causes the dissolved gases and water to vaporize and be extracted from the oil.
After degassing and dehydration, the oil passes through mechanical filters. These filters are designed to remove solid particles and sludge from the oil. The filtration can be a single or multi-stage process, using different grades of filter media to achieve the desired cleanliness level.
If the oil has degraded significantly, a process called regeneration may be employed. This involves passing the oil through columns filled with adsorbent materials such as Fullers Earth or activated alumina, which remove oxidation products and acids, restoring the oil's chemical properties.
Once the filtration process is complete, the oil is tested again to ensure that it meets the required standards for purity and insulating properties. Tests repeated might include those initially performed, plus additional checks for acidity and other properties based on specific requirements.
After confirming that the oil quality meets all specifications, it is either returned to the transformer (in the case of offline filtration) or continued in operation (for online filtration).
The contaminants removed from the oil, such as used filters and absorbents, must be disposed of according to environmental regulations to prevent pollution.
The entire process may vary slightly depending on the specific equipment used and the condition of the oil, but generally follows this sequence to ensure the transformer oil is effectively cleaned and restored, thus ensuring the transformer operates efficiently and safely.
 Benefits of Transformer Oil Filtration
Benefits of Transformer Oil Filtration