 Applications
Applications
Our organisation categorises electrical components based on specific purposes and voltage criteria, simplifying their selection for diverse applications.
 What is relay coordination study in an electrical system?
What is relay coordination study in an electrical system?

A relay coordination study in an electrical system is a critical analysis conducted to ensure the proper functioning of the system's protective devices, specifically relays, during fault conditions. It involves the calculation and setting of relay characteristics and timing, considering the operational characteristics of all equipment in the electrical network. It uses simulations of various fault scenarios to test and refine the settings, ensuring that the relays operate correctly under all conditions. The coordination study is an essential part of the design and maintenance of any power distribution or transmission system, as it directly impacts the system's safety, reliability, and efficiency.
 Why relay coordination is important?
Why relay coordination is important?

Ensuring proper coordination in electrical systems is crucial for various reasons that enhance the safety, reliability, efficiency, and performance of the power system. These are the key factors that highlight the importance of relay coordination:
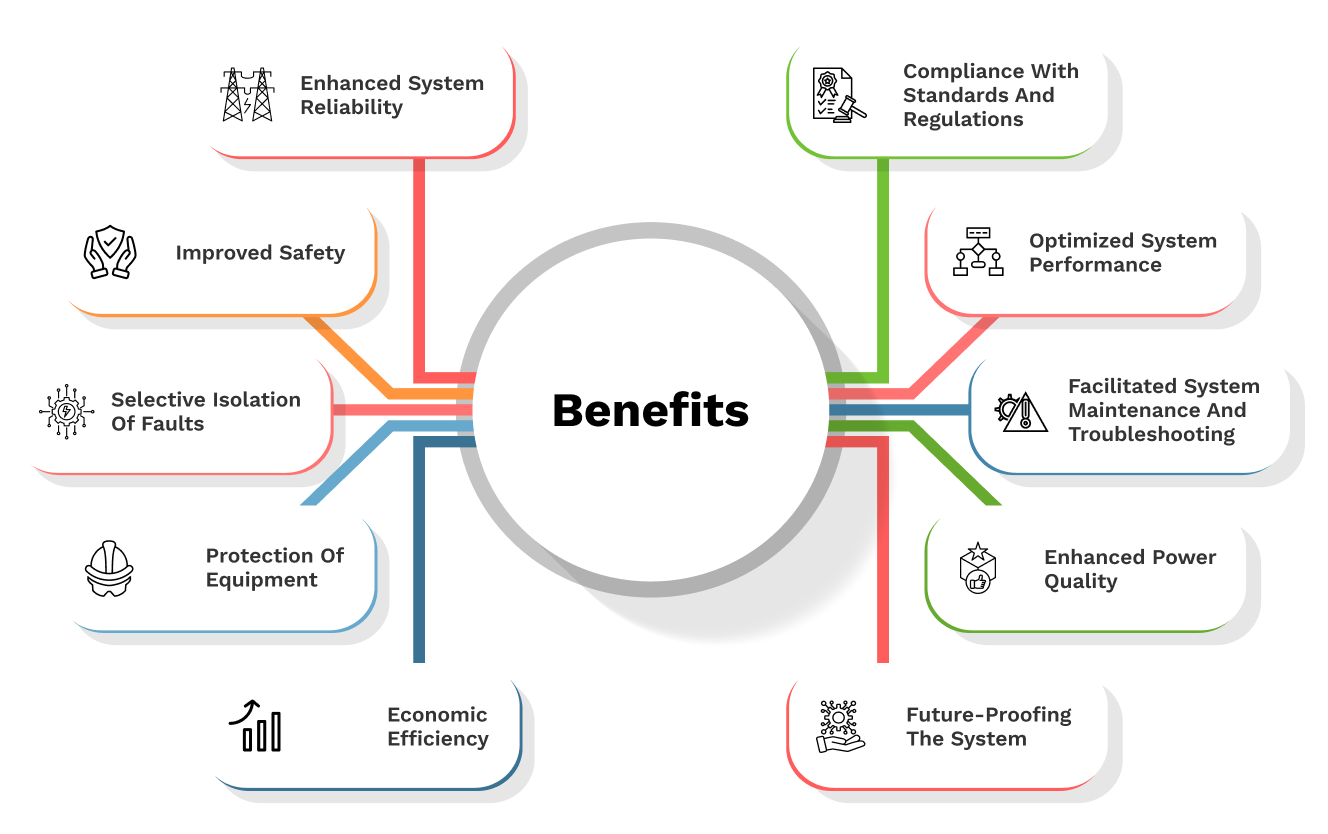
Ensuring proper coordination of relays is essential to isolate only the faulty section of the network while keeping the rest of the system running smoothly. By isolating selectively, system downtime is minimized and widespread power outages are prevented.
Relay coordination is crucial for safeguarding electrical equipment from damage due to overcurrents, short circuits, and other fault conditions by ensuring that only the essential protective devices are activated during a fault. This can help prolong the lifespan of the equipment and lower maintenance and replacement expenses.
Ensuring the safety of personnel working on or near the electrical system is crucial, and coordinated relay settings play a key role in preventing dangerous conditions that could lead to fires, explosions, or electric shocks.
Through prompt identification and containment of issues, relay coordination plays a crucial role in enhancing the stability and dependability of the power system. This is essential for critical infrastructure and services that rely on a consistent power supply.
Having a well-organized relay system can assist in precisely pinpointing the location and type of faults, simplifying the analysis and resolution of issues, ultimately enhancing system maintenance and troubleshooting procedures.
Ensuring proper relay coordination is a common necessity to meet national and international standards and regulations. These guidelines guarantee that electrical systems are planned and operated in a secure and dependable way.
Ensuring proper coordination of relays is crucial in preventing circuit breakers from tripping unnecessarily, which can result in operational losses and higher expenses. By making sure that protective devices only operate when needed, it helps to preserve economic efficiency and minimize energy waste.
 When to perform relay coordination?
When to perform relay coordination?

To guarantee the safety, dependability, and effectiveness of an electrical power system, relay coordination must be executed at a number of critical junctures through its lifecycle. The following are critical situations in which relay coordination is vital:
It's crucial to incorporate relay coordination from the start of designing and planning an electrical system. By ensuring that the protective devices are correctly chosen and adjusted based on the expected operating conditions and fault scenarios, it allows for the best possible system performance right from the start.
Modifying the electrical system, like expanding it or adding new equipment, can impact fault current levels and current distribution during faults. Following these modifications, it is essential to conduct a new relay coordination study to verify that the protective settings are still suitable for the updated system setup.
When you upgrade or replace significant equipment such as transformers, generators, or feeders, it can impact the overall impedance of the system and the fault current levels. This requires a review and adjustment of the relay settings to ensure proper coordination.
Major shifts in power distribution or consumption within the system, such as alterations in industrial processes, the introduction of significant loads, or network restructuring, can affect current balance and flow. This may necessitate a review of relay coordination.
It's a good idea to regularly check and confirm relay settings, even if the system configuration remains mostly the same. This guarantees that any deviation in relay performance or alterations in system conditions over time are taken care of.
If your operational experience, like nuisance tripping or failure to isolate faults correctly, indicates that the current relay coordination is not working well, it is important to conduct a thorough study to identify and fix these problems.
Specific intervals or conditions may need to be followed for relay coordination studies to comply with regulatory or insurance requirements and maintain safety and reliability standards.
 Who require Relay Coordination?
Who require Relay Coordination?

Power generation, transmission, and distribution companies require relay coordination to ensure the reliability and stability of the electrical grid. They need to minimize the impact of faults to prevent widespread outages and maintain service quality.
Plants and factories with complex electrical systems, especially those with critical operational processes or hazardous environments, rely on relay coordination to protect their infrastructure and ensure operational continuity.
Large commercial complexes, including shopping centers, office buildings, and hotels, need relay coordination for the safety of their electrical systems. This ensures protection against electrical faults and minimizes disruption to business operations.
These facilities require highly reliable electrical systems due to the critical nature of healthcare operations and the dependence on medical equipment. Relay coordination is crucial for ensuring power quality and reliability.
Given their critical role in hosting IT infrastructure and services, data centers require robust relay coordination to prevent power disturbances that could lead to data loss or service downtime.
Solar, wind, and other renewable energy installations need to integrate safely and reliably into the wider power grid or local electrical systems. Relay coordination ensures that faults within the renewable energy systems or in the grid do not lead to larger issues.
Universities, colleges, and research labs with significant electrical infrastructure require relay coordination to protect equipment, ensure safety, and maintain continuity of operations.
Public infrastructure projects, such as transportation networks, water treatment plants, and public lighting systems, also depend on relay coordination for the safety and reliability of their electrical systems.
These entities may require relay coordination studies to comply with safety and reliability standards. Insurance companies, in particular, might mandate such studies as part of the risk assessment process for underwriting policies.
 Procedure involved in conducting relay coordination study
Procedure involved in conducting relay coordination study

Carrying out a relay coordination study requires a methodical approach to guarantee that all protective devices in an electrical system function properly and effectively in case of faults. The typical process involves the following steps:
 Benefits of conducting relay coordination
Benefits of conducting relay coordination

 Standards
Standards
