Applications
Applications
Our organisation categorises electrical components based on specific purposes and voltage criteria, simplifying their selection for diverse applications.
 Energy Meter Testing
Energy Meter Testing

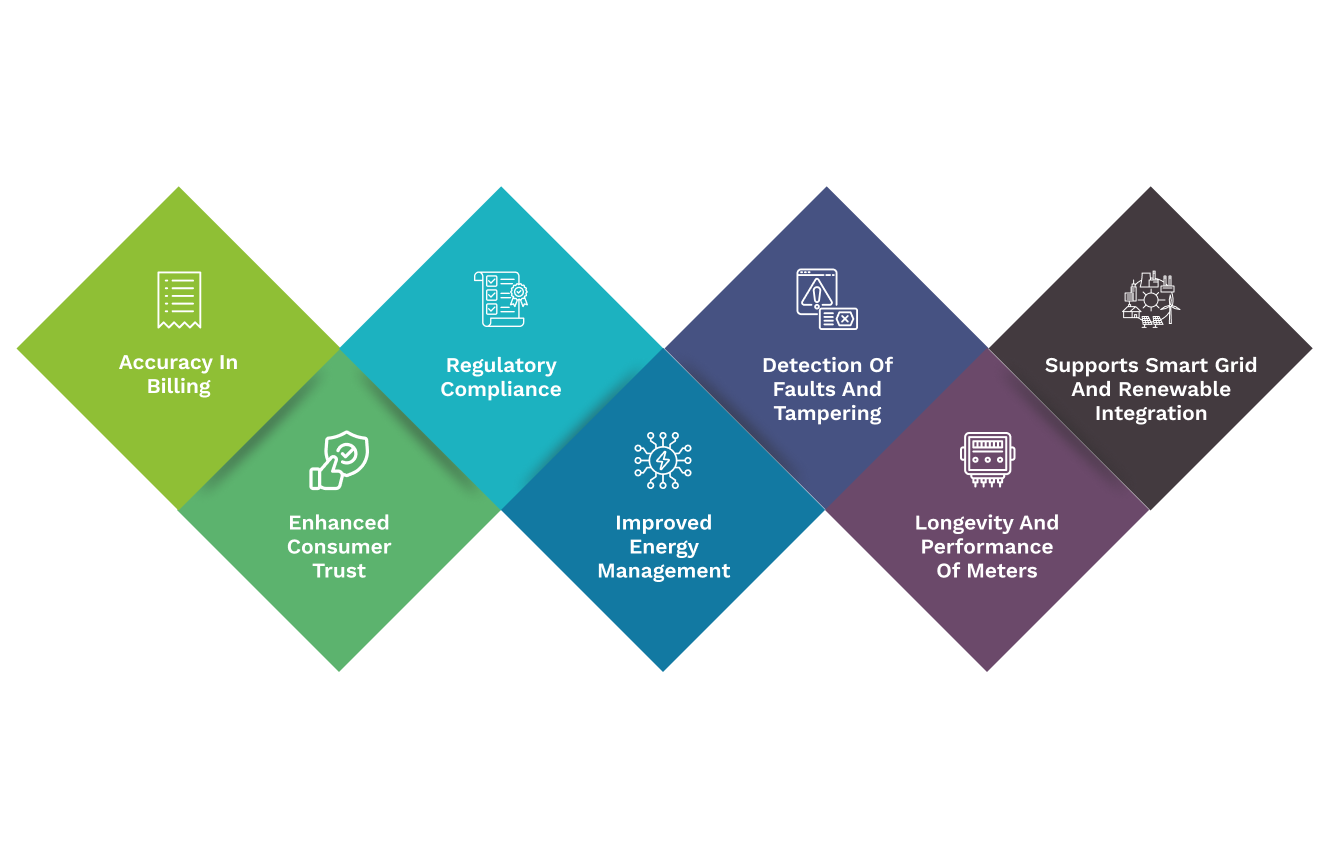
Energy Meter Testing plays a critical role in maintaining fair and transparent billing, protecting revenue, building consumer trust, supporting energy efficiency efforts, complying with regulations, and ensuring the safe and reliable operation of electrical systems. Regular testing and calibration of energy meters are essential to address these critical concerns and maintain the integrity of the electricity distribution system. Accurate meter data is the fundamental for the efficient and effective operation of electrical utilities. Are you looking for testing and calibration of energy meters, contact us by sending an email to reach@lselectricals.com or by filling the enquiry form.
 What is energy meter Testing and its Purpose?
What is energy meter Testing and its Purpose?

Energy Meter Testing in the electrical industry is defined as the process of verifying the accuracy, reliability, and efficiency of energy meters. These meters measure the amount of electrical energy consumed by a residence, business, or an electrically powered device, and accurate measurement is crucial for billing and energy management.
 Purpose of Energy Meter Testing
Purpose of Energy Meter Testing

The main purposes of conducting energy meter testing include:
To ensure that the energy meters are recording and reporting the energy use accurately. This is vital for fair billing and to avoid disputes between utility providers and customers.
To check if the meters meet the regulatory standards and specifications set by national and international standards organizations. Compliance ensures that the meters are safe to use and reliable.
To verify that the meters are operating efficiently and not leading to energy losses either due to technical faults or inaccuracies in measurement.
To ensure that the meters perform consistently over a long period under various environmental and load conditions.
To detect any tampering or bypasses which could lead to energy theft, affecting the revenues of utility companies and resulting in unfair costs to other consumers.
To identify early signs of meter degradation or failure, allowing for timely maintenance or replacement to ensure continuous and accurate metering.
 When is energy meter testing needed?
When is energy meter testing needed?

Energy meter testing is essential at several key points throughout the lifecycle of a meter, from its initial manufacture to its final decommissioning. Here are the main occasions when energy meter testing is typically required:
 Tests performed in testing of energy meter
Tests performed in testing of energy meter

On-site tests for energy meters are crucial for verifying that meters perform accurately and reliably in their actual usage environments. These tests are intended to ensure that meters not only function correctly under laboratory conditions but also under the varied and unpredictable conditions they encounter in the field. Here’s a detailed look at typical on-site tests conducted on energy meters:
This initial step involves verifying that the meter is installed correctly according to the manufacturer's guidelines and industry standards. It includes checking the wiring connections, proper grounding, and the physical security of the meter.
A thorough visual examination to check for any signs of damage, corrosion, or tampering that could affect the meter’s performance. This also includes ensuring that the meter's seals are intact.
These tests ensure that all meter functions work as expected. This includes checking the display, verifying remote communication capabilities (if applicable), and ensuring that auxiliary functions, such as time-of-use recording and demand metering, operate correctly.
This crucial test compares the meter's readings with a reference standard or a portable test unit to verify that it records energy consumption accurately. It usually involves applying known loads and comparing the meter’s readings against the test unit.
To assess the meter’s performance under different load conditions, varying levels of electrical load are applied. This helps ensure that the meter accurately measures low, medium, and high loads without deviation.
For smart meters, this test checks the integrity and security of the data communication system, ensuring that the meter can send and receive data correctly and securely from the utility for functions like billing and monitoring.
These tests verify that the meter correctly identifies and measures inputs across different phases and voltage levels, crucial for multi-phase systems.
Testing the meter’s ability to detect and record tampering attempts, such as magnetic interference or physical intrusion.
 Benefits of testing energy meters
Benefits of testing energy meters