 Applications
Applications
Our organisation categorises electrical components based on specific purposes and voltage criteria, simplifying their selection for diverse applications.
 What is relay testing in electrical system?
What is relay testing in electrical system?

Testing relays in electrical systems involves ensuring that they are functioning correctly and performing their intended tasks. Relays are essential devices that control the flow of electricity by opening and closing contacts in different circuits. When it comes to electrical systems, relays are essential for ensuring protection, control, and automation. Electrical equipment can be safeguarded against various electrical issues, such as overcurrents, undercurrents, overvoltages, undervoltages, and other faults, by effectively isolating the problematic component from the rest of the electrical network.
The objective of relay testing is to ensure that relays are in good working condition and correctly calibrated to protect the electrical system from damage due to faults or abnormal conditions, thus ensuring reliability, safety, and efficiency in electrical systems. Regular testing and maintenance are critical for the longevity and safety of electrical installations.
 Why do we need to do relay testing?
Why do we need to do relay testing?

Relay testing plays a vital role in various aspects, mainly in guaranteeing the security, dependability, and effectiveness of electrical systems.
Relays are essential for safeguarding electrical systems against potential hazards, such as overloads, faults, and abnormal conditions. Their primary function is to prevent equipment damage and, more importantly, ensure the safety of human life. By conducting relay tests, you can ensure that they function properly under various conditions, reducing the chances of electrical fires, equipment malfunctions, and other dangerous scenarios.
Regular testing and maintenance of relays is crucial for ensuring the smooth operation of electrical systems, preventing any unforeseen disruptions. Relays are specifically engineered to effectively handle faults, mitigate disturbances, and ensure the ongoing stability of the power system. Relays that are functioning correctly are crucial to ensure uninterrupted service and prevent expensive periods of inactivity.
Electrical equipment is carefully engineered to function effectively within designated voltage and current parameters. Relays play a crucial role in safeguarding the equipment from potential harm caused by electrical faults, including short circuits, overloads, and voltage spikes. Ensuring the proper functioning of relays is crucial to safeguard valuable and essential equipment from potential harm.
Relay testing is a proactive approach that aids in the early detection of possible problems, preventing system failures. Through early detection and prompt correction, maintenance teams can effectively avoid major issues that may result in costly repairs or replacements, ultimately saving valuable time and resources.
Regular testing and maintenance of electrical protection systems, including relays, is mandated by regulations and standards in various industries and regions. Adhering to these standards is crucial for maintaining safety and may also be necessary for insurance purposes or to fulfill contractual obligations.
Over time, the precision of relay settings may shift due to various factors such as environmental conditions, the passage of time, or alterations in the system setup. Testing confirms that the relay settings remain accurate and properly calibrated to the current system parameters, guaranteeing their reliable operation during fault conditions.
Testing is crucial for fine-tuning relay settings to achieve the optimal balance between protection and sensitivity. This requires making adjustments to the settings in order to avoid unnecessary interruptions caused by nuisance tripping, while still maintaining sufficient protection against actual faults.
 Who Needs Relay Testing?
Who Needs Relay Testing?

Power generation, transmission, and distribution companies need to regularly test relays to ensure the reliability and safety of the electrical grid.
Manufacturing plants, processing facilities, and other industrial operations that rely on complex electrical systems for their operations. Regular testing is necessary to prevent downtime and protect equipment.
Office buildings, shopping centers, and other commercial properties with significant electrical loads and complex systems require relay testing to protect infrastructure and ensure safety.
These facilities have stringent requirements for electrical reliability due to the life-saving equipment they operate. Relay testing is crucial to ensure uninterrupted power supply.
Given their critical need for uninterrupted power, data centers regularly test relays as part of comprehensive electrical system maintenance to prevent data loss and downtime.
Airports, subway systems, and other critical infrastructure components that depend on reliable electrical systems for safe operation.
These entities often conduct relay testing as part of their services to ensure that electrical installations meet design specifications and safety standards.
 When Relay Testing is Needed?
When Relay Testing is Needed?

To verify that relays are properly configured and functioning correctly before the system is fully operational.
Any time there are changes or upgrades to an electrical system, including adding new equipment or modifying existing circuits, relay settings may need adjustment, and their operation should be tested.
Following an electrical fault, relays should be tested to ensure they responded correctly and have not been damaged, ensuring they are ready for future operations.
Regularly scheduled testing (annually, biennially, etc.) as part of preventive maintenance programs to ensure ongoing reliability and to detect any potential issues before they lead to system failures.
To adhere to industry regulations and standards that may specify testing frequencies and procedures for electrical safety and reliability.
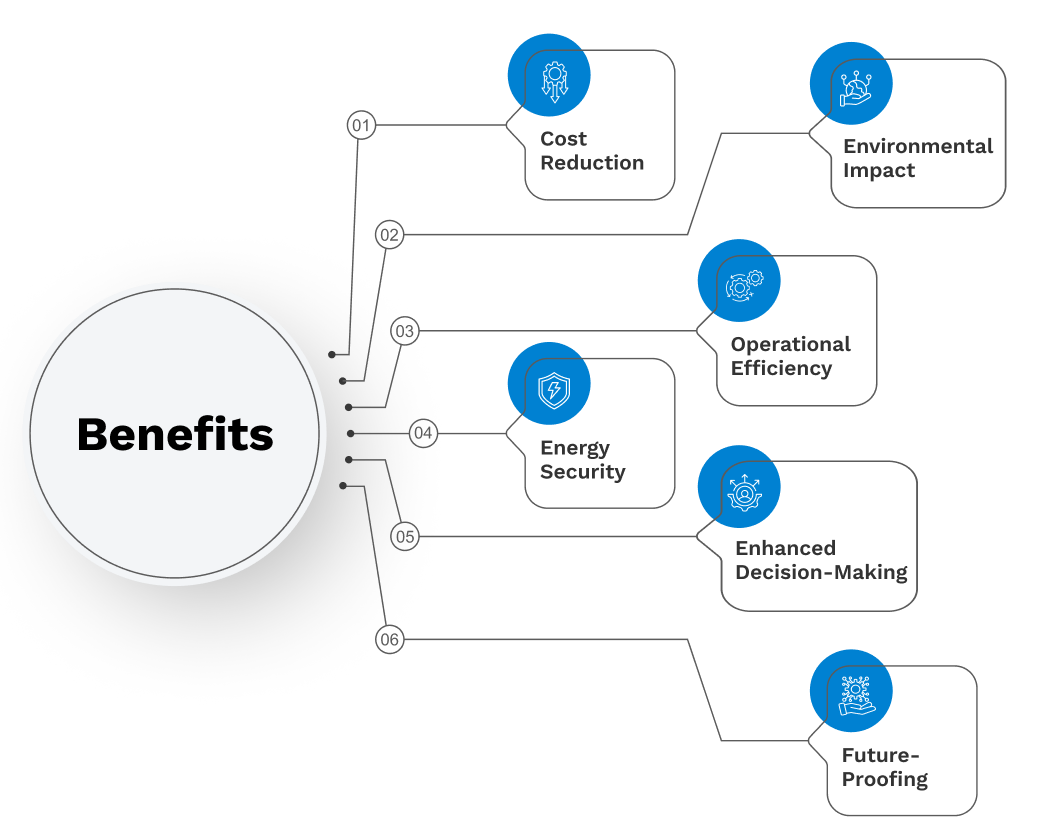
 What are the benefits associated with relay testing?
What are the benefits associated with relay testing?

 Procedure involved in testing of relays at site
Procedure involved in testing of relays at site

To verify that a relay is operating as intended within its specified limitations, it must undergo a thorough testing procedure when installed on-site. How this is done differs from one application to another, from one electrical system to another, and from one type of relay to another. As a general rule, onsite relay testing entails the following steps:
 Standards
Standards
