 Applications
Applications
Our organisation categorises electrical components based on specific purposes and voltage criteria, simplifying their selection for diverse applications.
 HV / LV Switchgear Services
HV / LV Switchgear Services

Low Voltage (LV) and Medium Voltage (MV) switchgear are key components in electrical distribution systems, designed to safely control, protect, and isolate electrical equipment. Here's a detailed look at each:
 Low Voltage (LV) Switchgear
Low Voltage (LV) Switchgear

Low Voltage switchgear is used in electrical circuits that carry voltages up to 1,000 volts AC. In some standards, the upper limit is defined as 600 volts. LV switchgear is crucial in applications ranging from residential and commercial buildings to industrial facilities. The primary functions of LV switchgear include:
Safeguarding the electrical circuit from overload and short circuits by using circuit breakers and fuses.
Enabling manual or automatic control of the electrical system. This can include switching operations for maintenance or operational needs.
Providing a means to isolate parts of the electrical system for maintenance and safety purposes.
Often integrated with advanced control systems that monitor electrical parameters like voltage, current, and power factor.
Common components of LV switchgear include circuit breakers, load break switches, fuses, and protective relays.
 Medium Voltage (MV) Switchgear
Medium Voltage (MV) Switchgear

Medium Voltage switchgear is used in systems that carry voltages between 1 kV and up to about 36 kV. These are typically used in large industrial plants, infrastructure projects, and electrical utility companies. The functions are similar to LV switchgear but are designed to handle higher voltages and therefore have additional specifications and safety requirements. Key functions include:
MV switchgear uses circuit breakers that can interrupt higher currents and deal with higher voltages, thus protecting the electrical system from faults effectively.
Provides capabilities for remote or automated control operations, often integrated with industrial control systems for efficient operations.
Ensures safety by isolating high voltage circuits during maintenance or faults.
Advanced monitoring systems in MV switchgear help in optimizing the performance and safety of the electrical distribution system.
MV switchgear components are often enclosed within metal-clad housing to provide additional safety and are equipped with technology like vacuum or SF6 (sulfur hexafluoride) circuit breakers for efficient operation.
 Services for LV and MV Switchgear
Services for LV and MV Switchgear

Services for LV and MV switchgear are crucial for ensuring reliable operation, safety, and compliance with electrical standards and include:
Proper setup and commissioning of switchgear.
Regular maintenance is vital to prevent unexpected failures and extend the life of the equipment. This includes routine inspections, cleaning, and testing of components.
Addressing and fixing faults or damage that may occur due to operational issues or environmental factors.
Updating old switchgear to modern standards with better performance and safety features.
Ensuring that all components function as intended before full-scale operation.
These services help maintain system integrity and reliability, ensuring that electrical distribution systems operate smoothly and efficiently.
 Why is it necessary?
Why is it necessary?

Performing services on Low Voltage (LV) and Medium Voltage (MV) switchgear is essential for several reasons, all of which contribute to the safety, reliability, and efficiency of electrical distribution systems. Here are the key reasons why these services are necessary:
Regular switchgear maintenance and service prioritize safety. Electrical systems, especially medium and high voltage ones, can cause shocks, fires, and explosions. Regular maintenance keeps switchgear protective devices working properly, reducing accidents and protecting people and property.
Modern structures, from commercial to industrial, depend on electrical systems. Switchgear maintenance ensures reliability and availability. Reliability is essential to avoid downtime, which is expensive directly and indirectly.
Standards and laws pertaining to national and international safety must be followed by electrical systems. Frequent servicing of switchgear aids in maintaining adherence to these standards, which frequently outline specifications for performance benchmarks, operating safety, and maintenance schedules. In addition to assisting in avoiding legal problems, compliance guarantees a uniform approach to the efficiency and safety of electrical systems.
Switchgear controls the flow of electricity and protects against overloads and short circuits. Without regular maintenance, the components of switchgear, such as circuit breakers and relays, may fail to operate as designed. Such failures can lead to severe electrical faults that might cause extensive damage to electrical equipment and the broader network.
Regular maintenance can significantly reduce the overall operational costs of electrical systems. By identifying and addressing potential issues early through routine servicing, expensive repairs and replacements can be avoided. Furthermore, well-maintained switchgear operates more efficiently, potentially reducing energy consumption and costs.
Regular servicing includes cleaning, lubrication, and the replacement of worn parts, which can significantly extend the lifespan of switchgear equipment. By prolonging the life of existing equipment, companies can defer the substantial capital expenditures associated with replacing large-scale electrical components.
Maintenance services often include the calibration of equipment to ensure it operates at peak efficiency. This can involve adjusting settings, updating firmware, or retrofitting components to improve functionality and efficiency.
In an era of rapid technological advancement, keeping electrical systems updated and capable of integrating with new technologies is crucial. Regular switchgear servicing can include system upgrades that incorporate newer technology, making it easier to adapt to future developments.
Performing regular services on LV and MV switchgear is not just a regulatory and operational requirement but a critical practice for ensuring the safe, efficient, and cost-effective operation of electrical distribution systems.
 When is it required to perform this service?
When is it required to perform this service?

The kind of equipment, usage patterns, ambient conditions, and industry norms all play a role in determining when it is best to service Low Voltage (LV) and Medium Voltage (MV) switchgear. Here are some broad recommendations regarding when to carry out these crucial services:
Regularly scheduled maintenance is one of the most effective ways to ensure switchgear reliability and longevity. The frequency of scheduled maintenance typically depends on:
Maintenance schedules can also be planned based on the operational hours of the switchgear. High-use environments might necessitate shorter intervals between maintenance sessions.
Advanced switchgear systems often include monitoring technologies that can alert operators to conditions indicating potential failure or the need for maintenance. These can include changes in:
Using this data, maintenance can be performed proactively before failures occur.
Regular visual inspections can reveal issues such as corrosion, accumulation of dirt and debris, or physical damage. These inspections can often be performed without shutting down the system and can help determine when more thorough maintenance is required.
Whenever a fault occurs, such as a circuit breaker trip that isn't routine, or after any outage, a thorough inspection and potentially more extensive maintenance may be necessary. These events can indicate underlying issues that need immediate attention to prevent further damage.
In facilities where operations are critical, such as hospitals, data centers, or manufacturing plants, switchgear servicing might be scheduled before and after any major operational changes or upgrades. This helps ensure that the switchgear will perform reliably under new operating conditions.
Some industries are subject to specific regulatory requirements that dictate maintenance schedules. Ensuring compliance might require inspections and servicing at intervals mandated by law or industry standards.
In areas where environmental conditions change significantly with the seasons, switchgear might require specific preparatory checks. For example, preparing for higher loads in summer due to air conditioning use or ensuring that outdoor equipment is ready for winter conditions.
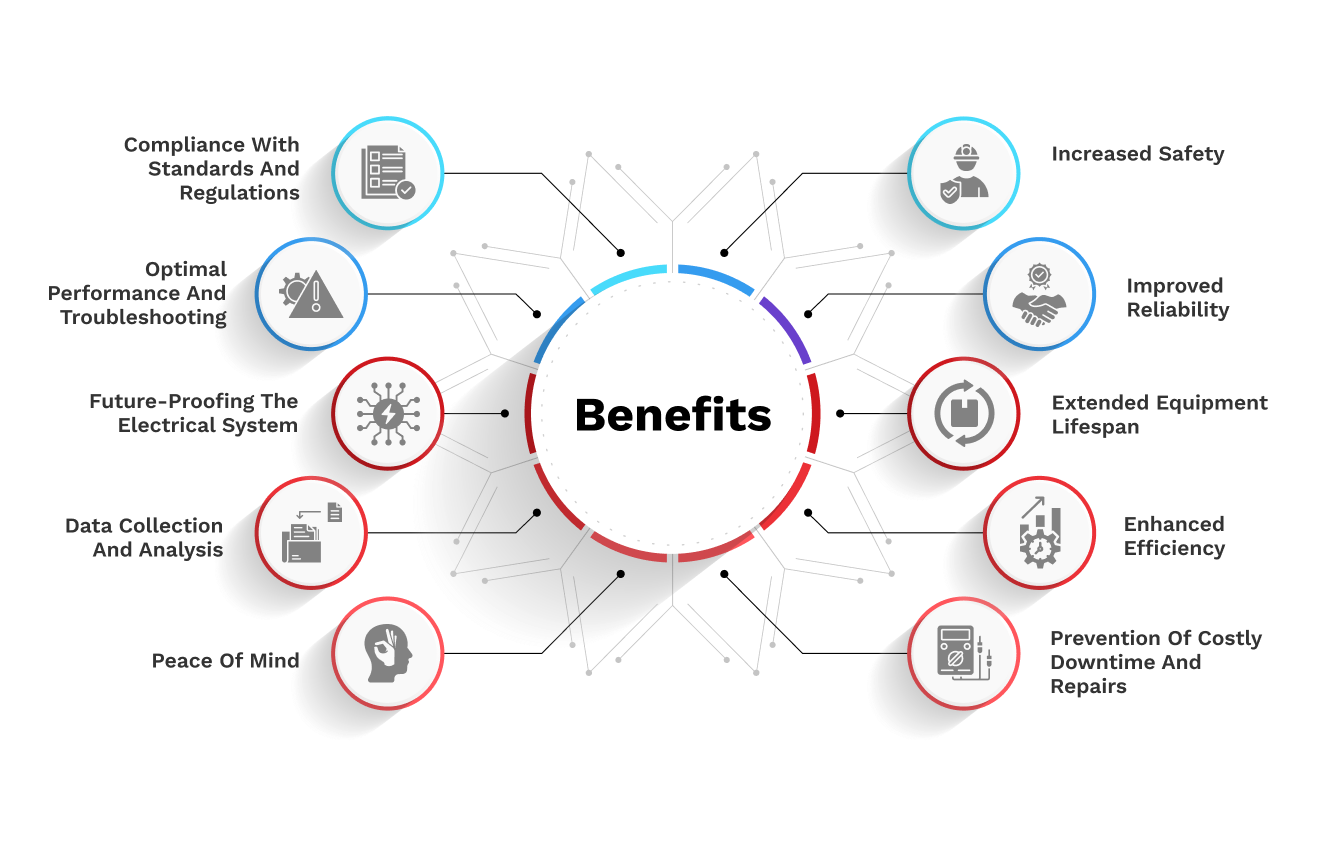
 What are the benefits on servicing?
What are the benefits on servicing?

 Scope of work involved in servicing of switchgear
Scope of work involved in servicing of switchgear

Servicing of Low Voltage (LV) and Medium Voltage (MV) switchgear involves a comprehensive range of tasks to ensure that all components function effectively and safely. Here’s a brief overview of the typical scope of work involved in switchgear servicing:
This scope of work ensures that the switchgear remains in optimal condition, reducing the risk of unplanned outages and extending the lifespan of the equipment while maintaining safety and compliance with regulatory requirements.